Table of Contents
In my personal experience, I’ve found that top-notch product lifecycle management (PLM) tools are absolute game-changers when it comes to overseeing every aspect of a product’s journey. Whether you’re dealing with a physical product or a service, the PLM tools I’ve used have been instrumental in guiding the entire process, from the initial concept and design phase, right through testing, planning, manufacturing, sales, customer support, ongoing updates, and ultimately, the moment a product becomes obsolete and is removed from the market.
Before I started using PLM software, managing all these stages was a significant challenge, especially when dealing with multiple geographic locations, various company branches, different product launch schedules, a range of product variations and updates, country-specific regulations, unique local branding strategies, and numerous other factors that can vary from place to place. From my experience, the importance of selecting the right PLM tool cannot be overstated. It’s the linchpin for efficiently managing your product portfolio, ensuring that every step of your product’s lifecycle runs smoothly and effectively.
What is PLM Software?
PLM software is a type of digital technology that was developed to assist in the management of the product lifecycle. There are several stages that a product goes through, beginning with its conception and continuing through its manufacturing until it reaches the conclusion of its existence. It is essential for businesses to manage the life cycle of their products since doing so enables them to track various data points that provide a clearer picture of the current standing and future trajectory of their product. In addition to this, it identifies a variety of various areas for development that they may work on to raise their profits, efficiencies, and overall productivity.
Best PLM Software Comparison Table
The PLM software application is a program that is utilized to manage the data associated with this entire lifetime and to integrate the data that is associated with it. Data pertaining to products can be managed via PLM software. Additionally, it is able to combine the data with other systems such as ERP, MES, and CAD.
| Feature | Issue tracking | Requirements management | Project management | Change management | Collaboration tools | Reporting and analytics | Deployment | Website Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jira | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Cloud, on-premise | Visit Website |
| SAP PLM | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Cloud, on-premise | Visit Website |
| Oracle Agile | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Cloud, on-premise | Visit Website |
| Siemens PLM | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Cloud, on-premise | Visit Website |
| Arena | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Cloud, on-premise | Visit Website |
Best PLM Software
PLM software shows crucial workflows, data, and insights throughout a product’s life, from brainstorming and designing to manufacturing and customer allocation, so everyone is on the same page for revisions.
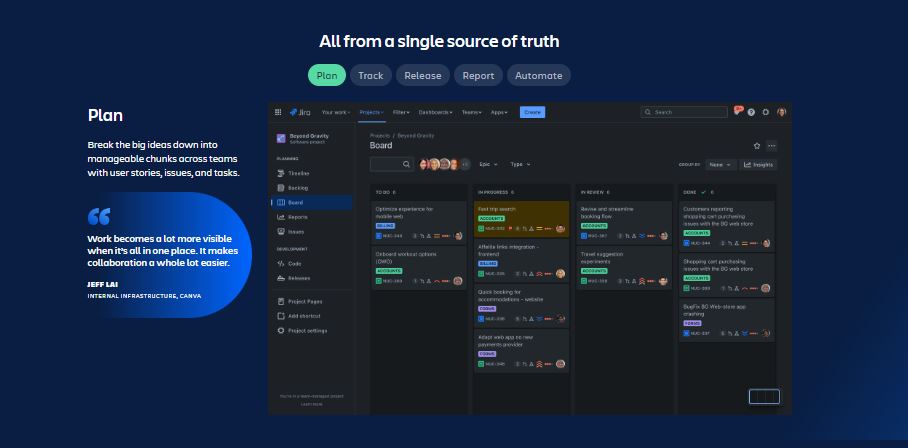
Jira
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Issue Tracking | Efficiently track and manage tasks |
| Agile Project Management | Plan, track, and report on agile projects |
| Custom Workflows | Customize workflows to suit your needs |
| Integration Options | Seamless integration with various tools |
| Reporting and Analytics | Gain insights with robust reporting |
Jira is an extremely flexible application that can be used for managing projects and keeping track of issues, in my experience. It is an excellent tool for assisting teams in properly planning and managing their work. I think one of its greatest strengths is its adaptability, which makes it appropriate for a wide range of business applications and kinds of projects.
The Good
- Versatile and customizable for different project types
- Strong integration capabilities with other software
- Excellent for agile project management
- Extensive reporting and analytics features
The Bad
- Can be overwhelming for small teams
- Learning curve for new users
- Licensing costs can be high for large organizations
SAP PLM

| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Lifecycle Management | End-to-end product lifecycle control |
| Product Data Management | Centralized data management for products |
| Collaboration Tools | Facilitate collaboration among teams |
| Compliance Management | Ensure product compliance with regulations |
| Analytics and Reporting | Data-driven insights for decision-making |
My prior work experience has been with the all-encompassing SAP PLM solution. It has proven to be useful for controlling all parts of a product’s lifespan, from the product’s conception all the way through to the product’s eventual retirement. This application has shown to be extremely helpful in the process of optimizing product development procedures, making it possible to collaborate effectively and efficiently manage data.
The Good
- Comprehensive product lifecycle management
- Integration with SAP’s ecosystem
- Powerful data management capabilities
- Robust compliance tracking and reporting
The Bad
- High implementation and maintenance costs
- Complex for smaller businesses
- Steeper learning curve for new users
Oracle Agile
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Collaboration | Collaborate on product development |
| Change Management | Efficiently manage changes in products |
| Quality Management | Ensure product quality and compliance |
| Project Portfolio Management | Align projects with business goals |
| Regulatory Compliance | Meet regulatory requirements with ease |
Oracle Agile PLM is yet another powerful PLM solution, in my opinion and based on my expertise. It is intended to speed up product invention and cut down on the amount of time needed to bring a product to market, two things that I have experienced firsthand. In the projects I’ve been working on, the toolkit it provides for managing product data, facilitating collaboration, and ensuring regulatory compliance has proven to be really useful.
The Good
- Strong collaboration features
- Comprehensive change and quality management
- Project portfolio alignment
- Compliance solutions for regulated industries
The Bad
- Expensive licensing and implementation
- May require specialized training
- Limited customization options
Siemens PLM

| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Design | Advanced product design and modeling |
| Digital Twin Management | Create and manage digital twins |
| Manufacturing Planning | Streamline manufacturing processes |
| Lifecycle Analytics | Analyze product performance and usage |
| Supplier Collaboration | Collaborate with suppliers efficiently |
For the purpose of digital product design and development, I’ve found the Siemens PLM software to be an extremely useful and comprehensive set of tools. It encompasses the entirety of the product lifetime, beginning with the conceptual design phase and ending with manufacturing. The projects that I’ve worked on since I started using this suite have seen significant improvements in terms of both teamwork and inventiveness.
The Good
- Cutting-edge product design capabilities
- Robust digital twin management
- Integrated manufacturing planning
- In-depth lifecycle analytics
- Effective supplier collaboration
The Bad
- High initial costs and complexity
- Better suited for large enterprises
- Requires skilled professionals
Arena

| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Bill of Materials (BOM) | Manage and track product BOMs |
| Document Control | Efficient document management |
| Quality Management | Ensure product quality and compliance |
| Supplier Collaboration | Collaborate with suppliers seamlessly |
| Regulatory Compliance | Meet regulatory requirements easily |
In addition to that, I’ve got the chance to work with Arena, a PLM solution that’s hosted in the cloud. When it comes to managing product information, quality, and compliance, this solution has shown itself to be highly effective. It makes collaboration between cross-functional teams and suppliers easier, which, in my experience, is one factor that contributes to the smooth creation of products.
The Good
- User-friendly interface
- Specialized in BOM and document control
- Strong quality management features
- Seamless supplier collaboration
- Compliance solutions for regulated industries
The Bad
- Limited scalability for very large organizations
- May lack some advanced manufacturing features
- Pricing can be restrictive for small businesses
Key Features to Look for in PLM Software
- Management of product data (PDM): CAD files, bills of materials (BOMs), specifications, and other related papers can all be managed and centralised with effective PDM tools.
- Control of Versions: Strong version control tools that keep track of changes to product designs and paperwork so that you can always find and go back to earlier versions when you need to.
- Managing the bill of materials: There are tools for making, updating, and analysing bills of materials. These tools allow multi-level BOMs, variants, and configurations.
- Management of Change: Full change management tools to keep track of and handle engineering changes, with approval processes and audit trails.
- Collaboration and automating work processes: Cross-functional teams can communicate and work together better with collaboration tools and workflow software that speeds up tasks like change requests and approvals.
- Taking care of documents: Product-related documents, like design specifications, compliance papers, and manuals, can be stored, organised, and managed with document management tools.
- Integration of CAD: Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software can be easily integrated, so engineers can use their favourite CAD tools while keeping data in sync with the PLM system.
How to Choose the Right PLM Software for Business
- Look at what your business needs: Start by learning about the specific PLM needs of your business. Write down the problems you want to solve with PLM tools and the goals you want to reach.
- Get key stakeholders involved: Key people from different areas, like engineering, product design, manufacturing, quality control, and supply chain management, should be involved. Their ideas are very important for choosing the best PLM system.
- Set your spending limits: Set up a clear budget for PLM software that includes not only the costs of installing it but also the costs of ongoing training, support, and maintenance.
- Find the features that you must have: Make a list of the most important features and functions that the PLM software must have based on what your business needs. Some of these are document control, change management, and CAD interface.
- Think about your integration needs: Find out how the PLM software will work with the other software you already have, like ERP, CAD, and CRM. For data to flow smoothly between areas, integration must be done well.
Questions and Answers
Considering that a CAD system’s sole purpose is to aid in the creation of a product’s design, its operations almost always come before the PLM phase. PLM is a more all-encompassing system than CAD, which only concentrates on the product’s technical drawings and can be thought of as a component of PDM. However, PDM can be considered a component of CAD.
You will learn about SolidWorks’ practical, three-step approach to PLM in this white paper. This strategy will help you manage your most significant intellectual asset, which is your product designs, in a secure and straightforward manner. You have the ability to enhance the data associated with your Digital Product and produce engineering data that is superior and more comprehensive for Operations.

