Table of Contents
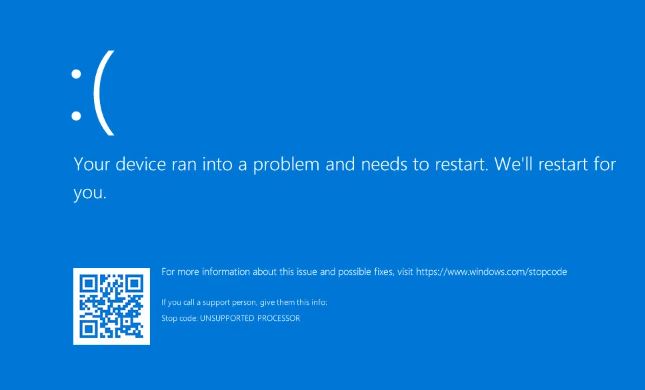
Learn how to Fix “Unsupported Processor Blue Screen” issue in Windows 10/11 in this guide. When you attempt to boot Windows on a processor or CPU that is not supported, you will encounter the blue screen of death error known as UNSUPPORTED_PROCESSOR. When you are attempting to install Windows 11 on hardware that does not meet the minimum system requirements of the new operating system, this is the most common scenario that can occur.
Not only that, but the BSOD error that occurs when the processor is not supported has recently become more noticeable on Windows 11 computers as a result of an optional update that was released by Microsoft. It is possible for users to encounter this error when they attempt to boot into Windows but are unsuccessful. The optional update in question is KB5029351, which also happens to be the root cause of the problem, which primarily affects users of MSI motherboards that are equipped with an Intel chipset interface.
A number of users have reported that they have been impacted by the optional update KB5029351, which was just recently made available in the preview channel. In addition to this, the error of an unsupported processor can also occur in other situations, and the BIOS firmware of your motherboard is typically the culprit in these situations. In this article, we will walk you through a variety of approaches that you can implement in order to find a solution how to Fix “Unsupported Processor Blue Screen” issue in Windows 10/11.
Causes of the “Unsupported Processor Blue Screen” issue in Windows 10/11
- Incompatible Processor Architecture: The most straightforward cause is that the installed version of Windows is not compatible with the architecture of the processor. For example, running a 64-bit version of Windows on a 32-bit processor or vice versa can trigger this error.
- Outdated Processor Drivers: Outdated or incompatible processor drivers can lead to compatibility issues with the operating system. Updating drivers to the latest versions may resolve the problem.
- Unsupported Features: Newer versions of Windows may require specific processor features that older processors lack. If the processor does not support certain instructions or features required by the operating system, it can result in a blue screen error.
- BIOS/UEFI Firmware Issues: Outdated or incompatible BIOS/UEFI firmware can lead to compatibility problems with the operating system. Updating the firmware to the latest version may resolve these issues.
- Hardware Virtualization: Some versions of Windows 10/11 require hardware virtualization support. If the processor lacks this feature or it’s not enabled in the BIOS/UEFI settings, it can trigger the “Unsupported Processor” error.
- Installation Media Issues: If the Windows installation media is corrupt or incomplete, it may not properly recognize or support the processor, leading to blue screen errors.
How to Fix “Unsupported Processor Blue Screen” issue in Windows 10/11
Update Windows
- Press Windows Key + I to open Settings.
- Navigate to Update & Security.
- Click on Windows Update.
- Select Check for updates and install any pending updates.
Install Microcode Updates
- Visit the official website of your processor manufacturer.
- Download the latest microcode updates for your processor model.
- Install the updates according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Update Device Drivers
- Press Windows Key + X and choose Device Manager.
- Locate the processor under the Processors category.
- Right-click on the processor and select Update driver.
- Choose Search automatically for updated driver software.
BIOS/UEFI Update
- Identify your motherboard model.
- Visit the motherboard manufacturer’s website.
- Download the latest BIOS/UEFI update.
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to update your BIOS/UEFI.
Disable Hyper-Threading (if applicable)
- Access BIOS/UEFI settings during system startup.
- Locate the Hyper-Threading option and disable it.
- Save changes and exit the BIOS/UEFI.
Perform a Clean Boot
- Press Windows Key + R, type “msconfig,” and press Enter.
- Navigate to the Services tab and check “Hide all Microsoft services.”
- Click on “Disable all” and then go to the Startup tab.
- Click on “Open Task Manager” and disable each startup item.
- Restart your computer.
Conclusion
On your Windows 10 or 11 computer, coming across the dreaded “Unsupported Processor Blue Screen” error can be an extremely frustrating experience. This problem frequently occurs as a result of compatibility issues between the operating system and the processor that you choose to use. You will be relieved to know that there are a number of actions you can take to rectify this problem and restore your system to its normal state.
Questions and Answers
In order to upgrade to Windows 11 on hardware that is not supported, use the Registry. In spite of the fact that it is not supported, Microsoft has published a workaround that allows users to continue the setup process by editing the Registry in order to circumvent the requirements of Windows 11. But the computer must have a TPM 1.2 chip and UEFI firmware that has Secure Boot enabled in order to function properly.
However, if you continue with the installation of Windows 11, your personal computer will no longer be supported and will no longer be eligible to receive updates. Damages to your personal computer that are caused by incompatibility are not covered by the warranty provided by the manufacturer.
A significant distinction between Windows 11 and Windows 10 is the design of the operating system. Windows 11 features a user interface that is more reminiscent of a Mac, with pastel colours, rounded corners for all windows, and a cleaner interface than its predecessor. A clean environment for work and play was created by Microsoft by simplifying the user interface (UI) as much as possible.
faster than one gigahertz (GHz) and containing two or more cores on a 64-bit processor or system on a chip (SoC) that is compatible with the processor. Memory must be at least four gigabytes (GB) in size. Storage: having a disc space of at least 64 gigabytes available. Over time, there may be an increase in the amount of storage space required for updates and to enable particular features within the operating system.

